Maximizing the 5G Effect: New Business Models, Use Cases and Hurdles
- By Saurabh Agrawal, Utpal Mangla and Mathews Thomas, IBM
- February 20, 2023

5G promises a new era of digital transformation globally. It improves on previous 4G networks, especially in highly-dense areas like malls/stadiums or mobile and dynamic situations by providing continuity, higher data rates, lower latency and a high number of simultaneous connections.
As a result, companies are embracing high-speed 5G as a key enabler of their digital transformation journey and are also looking to monetize their investments. This digital transformation will help unify and streamline enterprise assets — healthcare devices, vehicles, factory equipment, etc.
5G is also a key driver for IoT applications by enabling the ability to connect to a large number of devices with more stringent energy and transmission constraints. And there is a correlation between 5G and other new digital technologies like AI, big data, machine learning, IoT, cloud computing, edge computing, blockchain, virtual reality, augmented reality, etc.
New business models
As a result, we believe that the deployment of 5G networks and its integration with new technologies are expected to create new business models, accelerate digitalization and generate new revenue streams across a wide range of industries. Below are some of the key B2B, B2C, and B2X opportunities:
B2B (Business-to-Business) models:
- Network infrastructure providers: Companies that manufacture and supply 5G network infrastructure components, such as antennas, base stations, and routers.
- Network service providers: Companies that provide 5G network services, such as network design, deployment, and management, to other businesses.
- IoT solution providers: Companies that develop and provide IoT-based solutions and services to other businesses, leveraging 5G's high-speed and low-latency connectivity.
B2C (Business-to-Consumer) models:
- Consumer device providers: Companies that manufacture and sell 5G-enabled smartphones, laptops, and other consumer devices.
- Mobile network operators: Companies that provide 5G mobile network services to consumers, such as voice, data, and internet services.
- AR/VR content providers: Companies that develop and provide AR/VR-based content and experiences for consumers, leveraging 5G's high-speed and low-latency connectivity.
B2X (Business-to-Anything) models:
- Autonomous vehicle providers: Companies that develop and provide autonomous vehicles and related services, leveraging 5G's low-latency and high-speed connectivity.
- Edge computing providers: Companies that provide edge computing solutions and services, leveraging 5G's low-latency and high-speed connectivity to enable processing and storage to be located closer to the end user.
- Healthcare solution providers: Companies that develop and provide healthcare solutions, such as telemedicine and remote patient monitoring, leveraging 5G's high-speed and low-latency connectivity.
The above are a few examples of the many potential B2B, B2C, and B2X models for 5G. By leveraging these new business opportunities, companies can tap into the growing demand for 5G services and solutions, driving digital transformation and innovation in the years ahead.
New industry use cases
5G enables several industry use cases by providing the necessary high-speed, low-latency, and high-bandwidth connectivity that these applications require
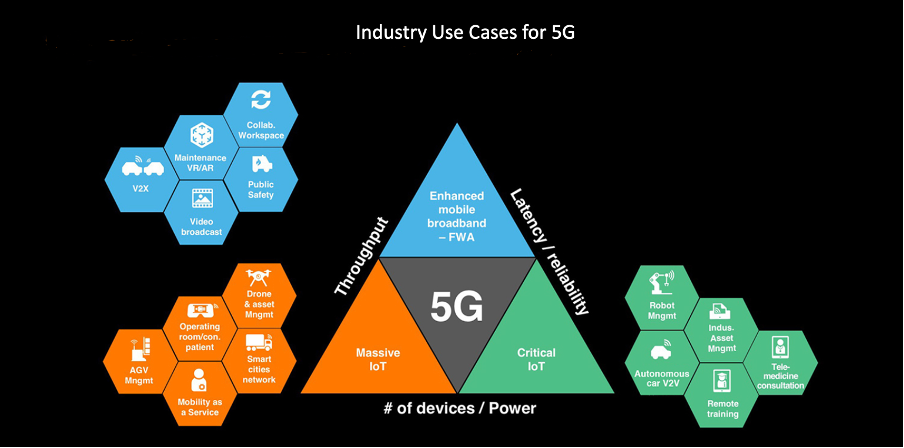
Some of these include
- Healthcare: 5G can be used to enable telemedicine and remote monitoring, enabling healthcare providers to deliver medical services to patients regardless of their location. It can also support virtual reality and augmented reality applications, enabling improved medical training and treatment planning.
- Manufacturing: 5G can be used to support industrial automation and control, enabling manufacturers to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality. It can also support predictive maintenance, enabling manufacturers to identify and fix potential problems before they occur.
- Automotive: 5G can be used to support autonomous vehicles, enabling vehicles to communicate with each other and with the infrastructure to enhance safety and improve the overall driving experience.
- Retail: 5G can be used to enable augmented reality and mixed reality applications, enabling retailers to offer customers a more immersive shopping experience and improve product visualization.
- Energy: 5G can be used to support remote monitoring and control of critical infrastructure, such as power plants and pipelines, enabling energy providers to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance safety.
- Telecommunications: 5G can be used to offer enhanced mobile broadband services, enabling telecom providers to offer improved and more personalized services to their customers.
- Public Safety: 5G can be used to support critical communications for first responders, enabling them to respond to emergencies more effectively and efficiently.
While there are huge numbers of use cases across industries, there are some challenges associated. They include device interoperability, increased threats from cyberattacks, stricter regulations and the cost for upgrading the existing infrastructure. Overcoming these challenges will be crucial for widespread adoption and success.
Rebalancing the monetization equation
While 5G offers a huge digital transformation potential, monetizing its investment is equally important for operators. 5G offers significant opportunities for digital transformation and monetization, enabling organizations to drive business growth, improve operations, and create new revenue streams. However, organizations also need to carefully consider their strategies and investment priorities to maximize the benefits of 5G and ensure long-term success.
This article was jointly written by Saurabh Agrawal, practice leader for network cloud, 5G and edge; Utpal Mangla, IBM’s general manager for industry EDGE Cloud on IBM Cloud Platform; Mathews Thomas, IBM’s distinguished engineer.
The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of CDOTrends. Image credits: iStockphoto/pcess609; chart: Orange Business Services









